Concurrency in Java
-
What is concurrency?
- Concurrency is the ability of different parts or units of a program, algorithm, or problem to be executed out-of-order or in partial order, without affecting the outcome
-
How are concurrent programs executed on a single CPU?
- Using time-slices
-
Distinguish between concurrency and parallelism
- Concurrency can be thought of as a way of structuring a program so that two threads can start, run and complete in overlapping time periods
- Parallelism is the runtime behavior of some concurrent programs where two or more threads are running simultaneously
-
Differentiate processes and threads
- Can a process access data of another process?
- Can a thread access data of another thread?
-
What are the two main problems when dealing with thread?
- Visibility
- Access
-
What is the visibility problem?
-
What is the access problem?
-
What does access and visibility problems lead to?
-
What is starvation
-
What is fairness
-
What are the three causes of starvation in Java
-
What is multitasking
-
What is multi-threading
-
What is the lineage of multi-threading and multitasking
- Time sharing system
-
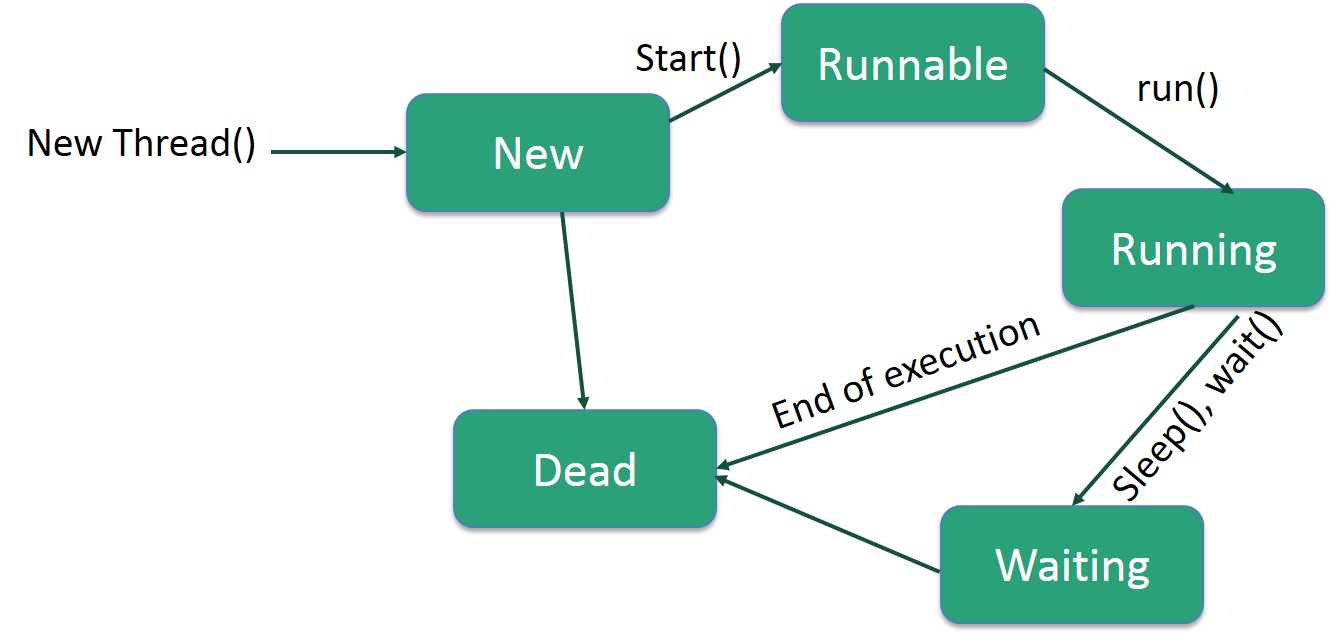
Draw the life cycle of a Java thread
-
What are the two states of an active thread?
- Running
- Runnable
-
How to move from running to runnable?
- using the
yield()method
- using the
-
What does
yielddo?yieldindicates to the scheduler that the current thread is willing to relinquish its current use of the processor but it would like to get back to running ASAP- The scheduler is free to schedule it whenever it wants
-
What are the two types of
waitin Java threads? -
What is the range of Java thread priorities and give the name of the constants
MIN_PRIORITY=> 1MAX_PRIORITY=> 10
-
What is the value given by default to thread and the name of the constant that identifies it
NORM_PRIORITY=> 5
-
Can thread priorities guarantee the order of execution
- No. It is platform-dependent
-
What method is used to set the priority of a thread?
setPriority()
-
How do you create a concurrent program in Java using the
Runnableinterface?- Create a class that implements the
Runnableinterface and implement therun()method - Create a
Threadobject with the constructor signature ofnew Thread(Runnable obj, String threadName) - Call the
start()method
- Create a class that implements the
-
How do you create a concurrent program in Java extending the
Threadclass?- Create a class that extends the
Threadclass - Override the
run()method - Create an object of the above class and call the
start()method
- Create a class that extends the
-
What is the preferred way to do concurrency in Java -
ThreadvsRunnable?- Implementing
Runnableis the preferred way to do it - Reasons
- From a OOP POV we are not trying to overwrite or extend any behavior of the
Threadclass. Rather we just giving it something to run. - So Composition is the proper way to do it.
- Another key things is Inheritance. Java doesn’t support multiple Inheritance. So if we inherit from the
Threadclass we can’t inherit from any other classes. But this is not the case if we are implementing theRunnableinterface class MyClass extends MyParent implements Runnableis possible
- From a OOP POV we are not trying to overwrite or extend any behavior of the
- Implementing
-
Mention some of the methods on the
Threadclasssuspendstopresumewaitnotify
-
How is
suspend()andresume()used- The thread is suspended until the
resume()method is invoked
- The thread is suspended until the
-
How is
wait()andnotify()used- The thread is suspended until the
notify()method is invoked on the object’s monitor
- The thread is suspended until the
-
What is the difference in using
wait(), notify()andsuspend(), resume()suspend(), resume()stop and start the thread- The purpose of
wait(), notify()is completely different.wait()is used to wait for something to happen. It is usually used for synchronization
-
How do you scale when you have many threads to execute?
java.lang.Runnabledoesn’t scale well- One thread for each task may add so much overhead that the point of multi-threading is moot
- The solution is the use of thread pools
- In Java this can be accomplished by implementing
java.util.concurrent.Executorinterface java.util.concurrent.ExecutorServiceinterface is used to control the execution of the thread pool
-
How do you declare a thread-safe method in java? -
publicsynchronizedvoid myMethod() -
How does a synchronized method guarantee mutual exclusion? - Locks
-
The lock acquired for an instance method is ? - object
-
The lock acquired for an static method is ? - Class
- What are synchronized blocks?
- They are a similar concept to a synchronized function
- The lock of the object reference given will be acquired and mutual exclusion will be ensured
- What are synchronized blocks?
-
Differentiate between
LockandReentrantLock-Lockis an interface -ReentrantLockis a concrete class that implementsLockplus some additional methods -ReentrantLock, as suggested by its name, is re-entrant meaning a process can acquire the lock held by itself without deadlocking- How to create fair locks in java?
- Instantiate the
ReentrantLockobject withtrueas a parameter
- Instantiate the
- How to create fair locks in java?
-
We know the signature of the
runispublic void run()meaning nothing is returned. Suppose you want the results of the computation to be returned. How to accomplish this? - Instead of using theRunnableinterface, implement theCallableinterface -
What is the
Futureobject?- Used to check the status of a
Callableand retrieve the results
- Used to check the status of a
-
What method would you use to get the results of a
Callableget()
-
What is the syntax used for
FuturewithCallable?Future<type> myVar = executor.submit(threadObj)
-
What is the way to implement truly parallel computation in java?
- Using the
ForkJoinTaskabstract class
- Using the
-
What are the two concrete classes under
ForkJoinTask?RecursiveActionRecursiveTask
-
What is the difference between
RecursiveActionandRecursiveTaskRecursiveTaskreturns the results
-
What does the
invoke()method do?- It first calls the
fork()and then waits tojoin()
- It first calls the
-
What is the method that is overridden in the
ForkJoinTask?- The
computemethod should be overridden
- The
-
We know that to efficiently use many thread we use thread pools. How to use those when using the Fork-Join framework?
ForkJoinPoolshould be used