../
Week Two
Introduction to Hadoop
What is Hadoop
- Framework to process huge amounts of data
- Set of open-source programs
History
- Born from the Nutch search engine
Components of Hadoop
- HDFS
- MapReduce
- YARN
Challenges
- Transactions
- Non-parallel tasks
- Dependencies
- Suppose one record has to be processed before another
- Low latency data
- Lots of small files
- Intensive calculations with little data
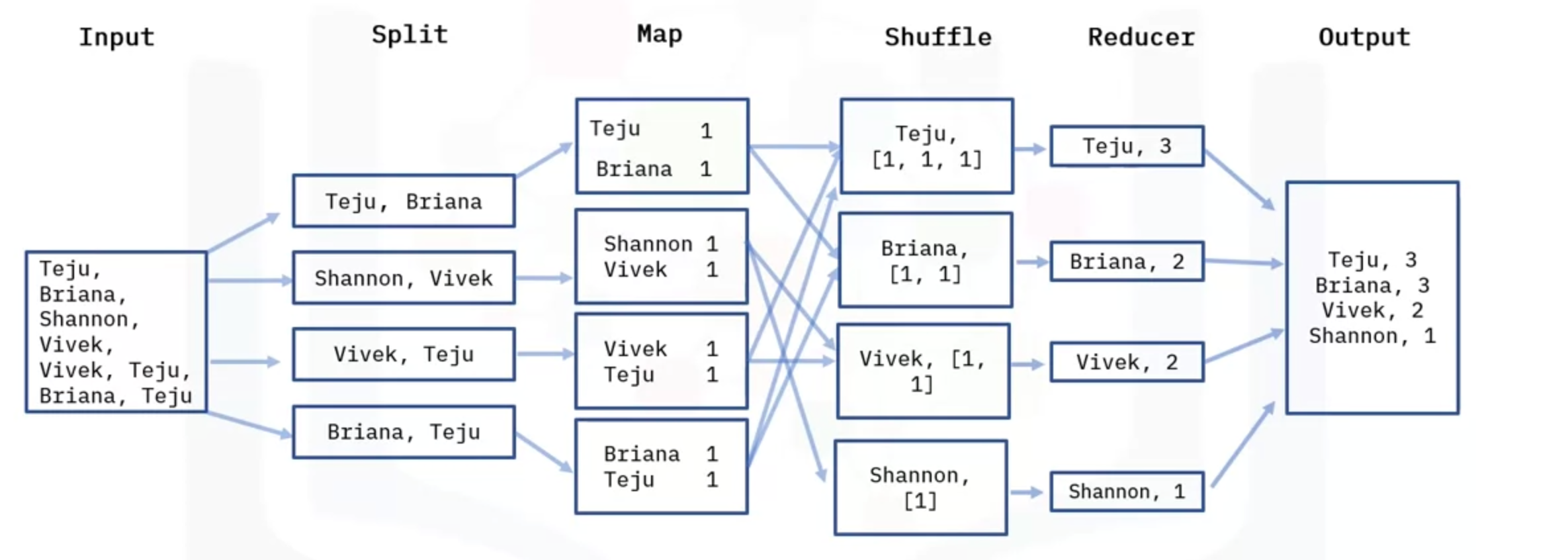
Intro to MapReduce
- MapReduce is a programming model
Hadoop Ecosystem
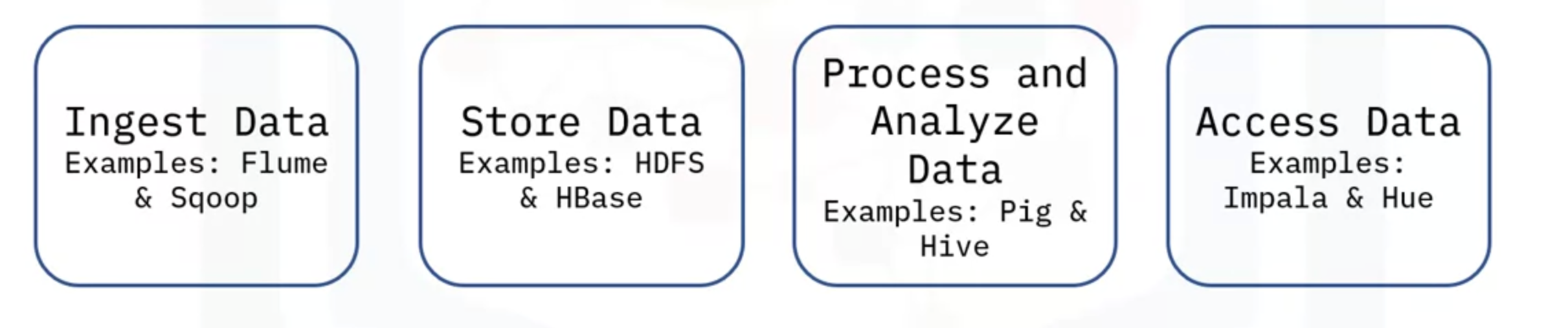
- Flume
- Data flow
- Sqoop
- Non-relational to relational mappers
- Can generate MapReduce code
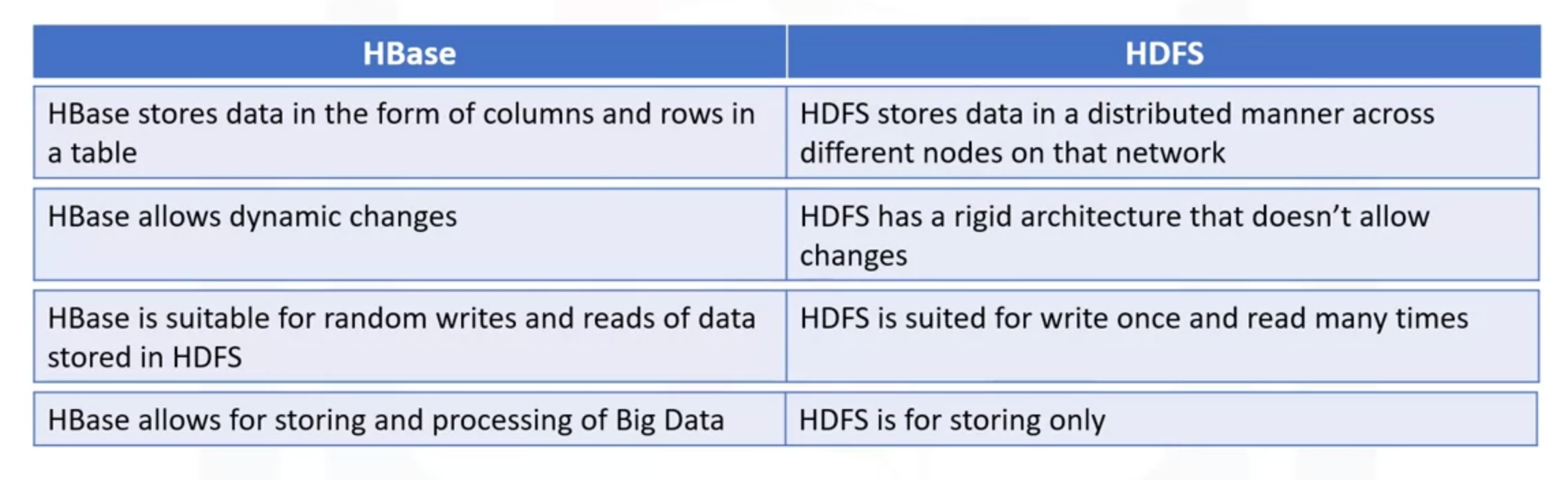
HDFS
- Block
- Smallest unit of data in HDFS
- Larger data is broken down into blocks
- usually 64 or 128MB
- But if the data is smaller then it can be stored as such
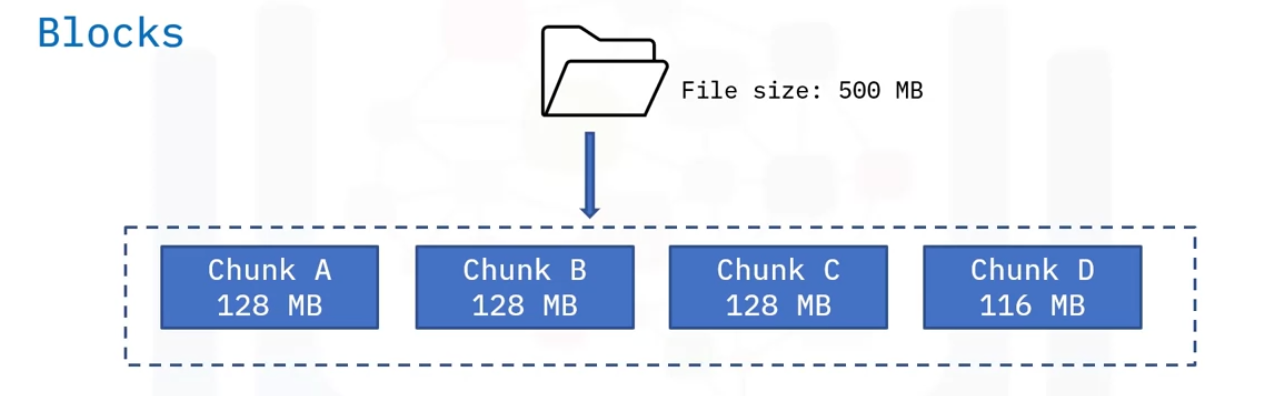
- No need to pad smaller data to make it to the block size
- Node
- A single computer that stores data
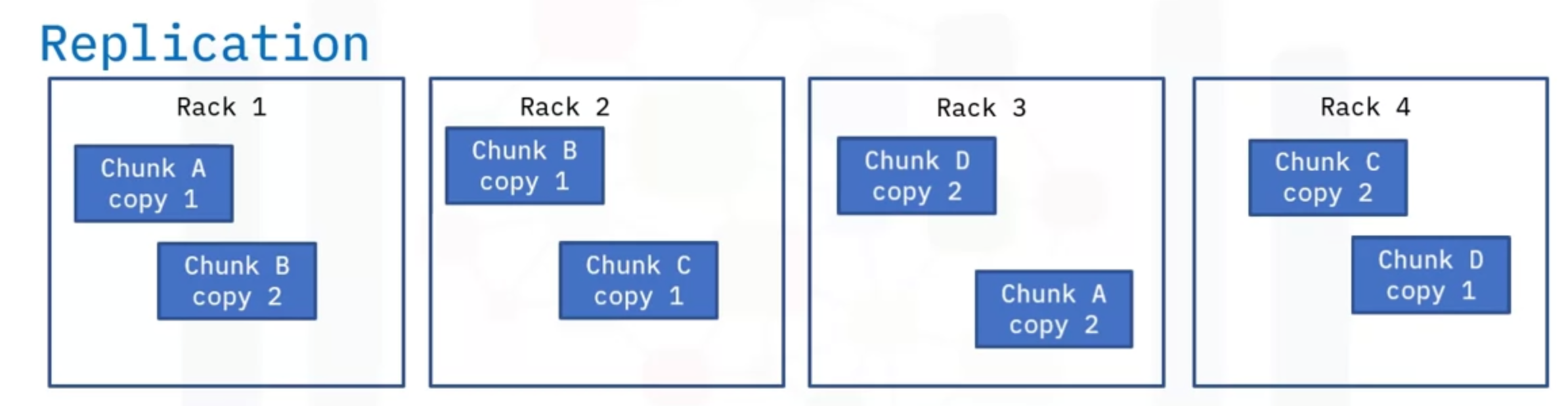
- Hadoop follows Primary-Secondary architecture
- The NameNode stores the metadata and instructs the DataNodes what to do
- NameNode always picks DataNodes that are closer by or in the same rack.
- This is called as Rack Awareness in HDFS
- The data replication is also done with rack awareness
- This is done by keeping track of rackID
- Read/Write
- Write once, read many
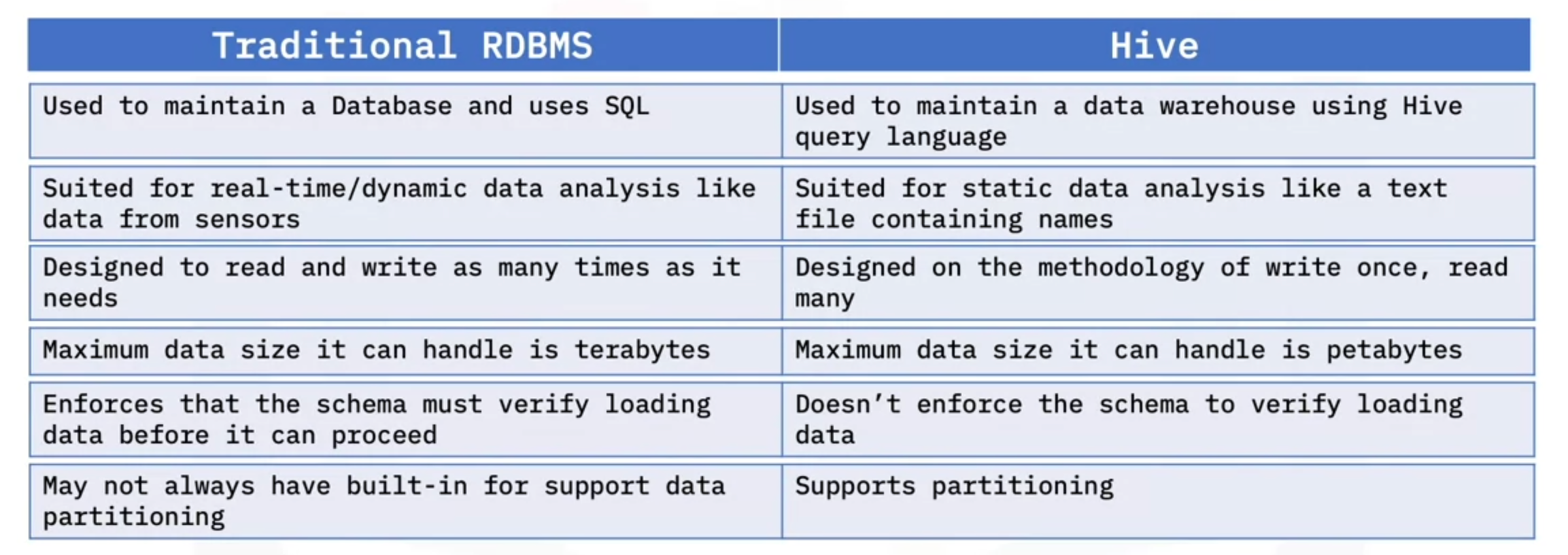
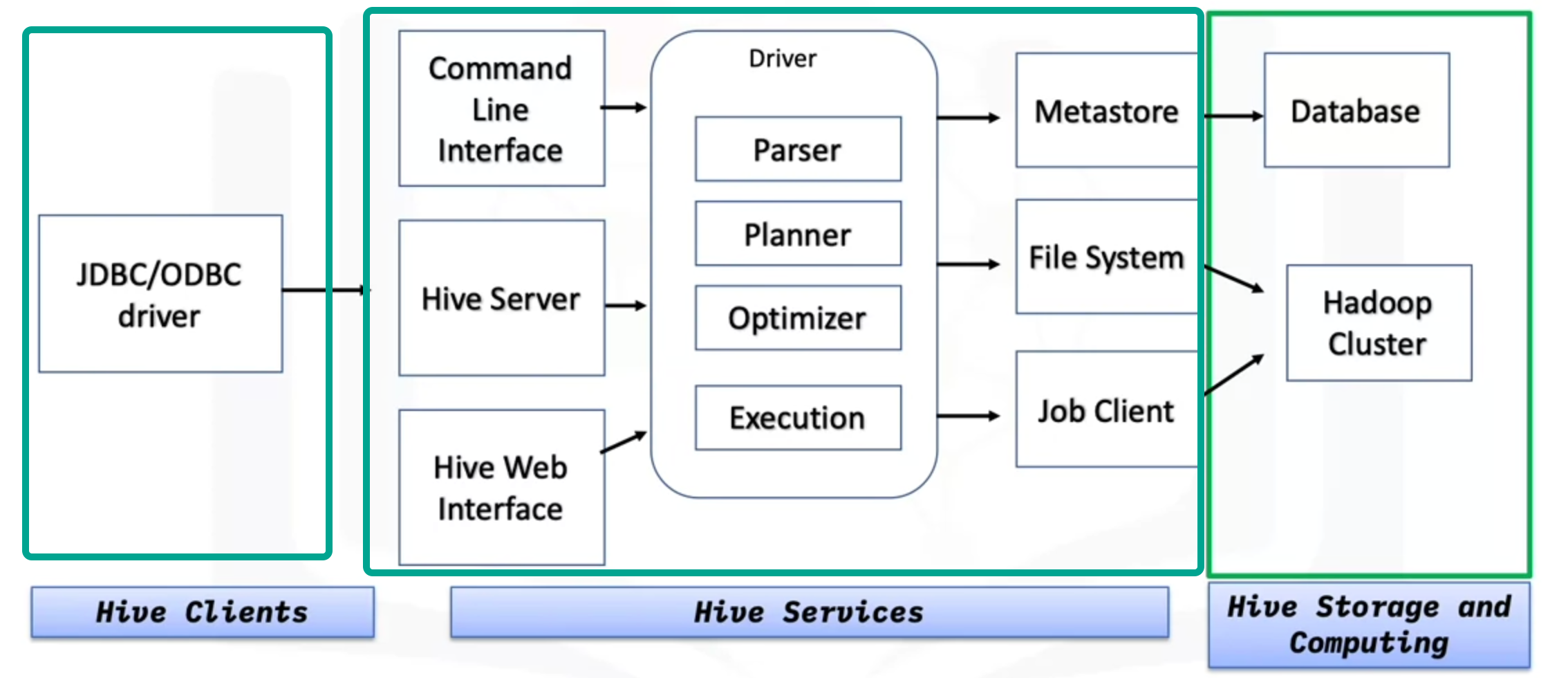
HIVE
- RDBMS for big data
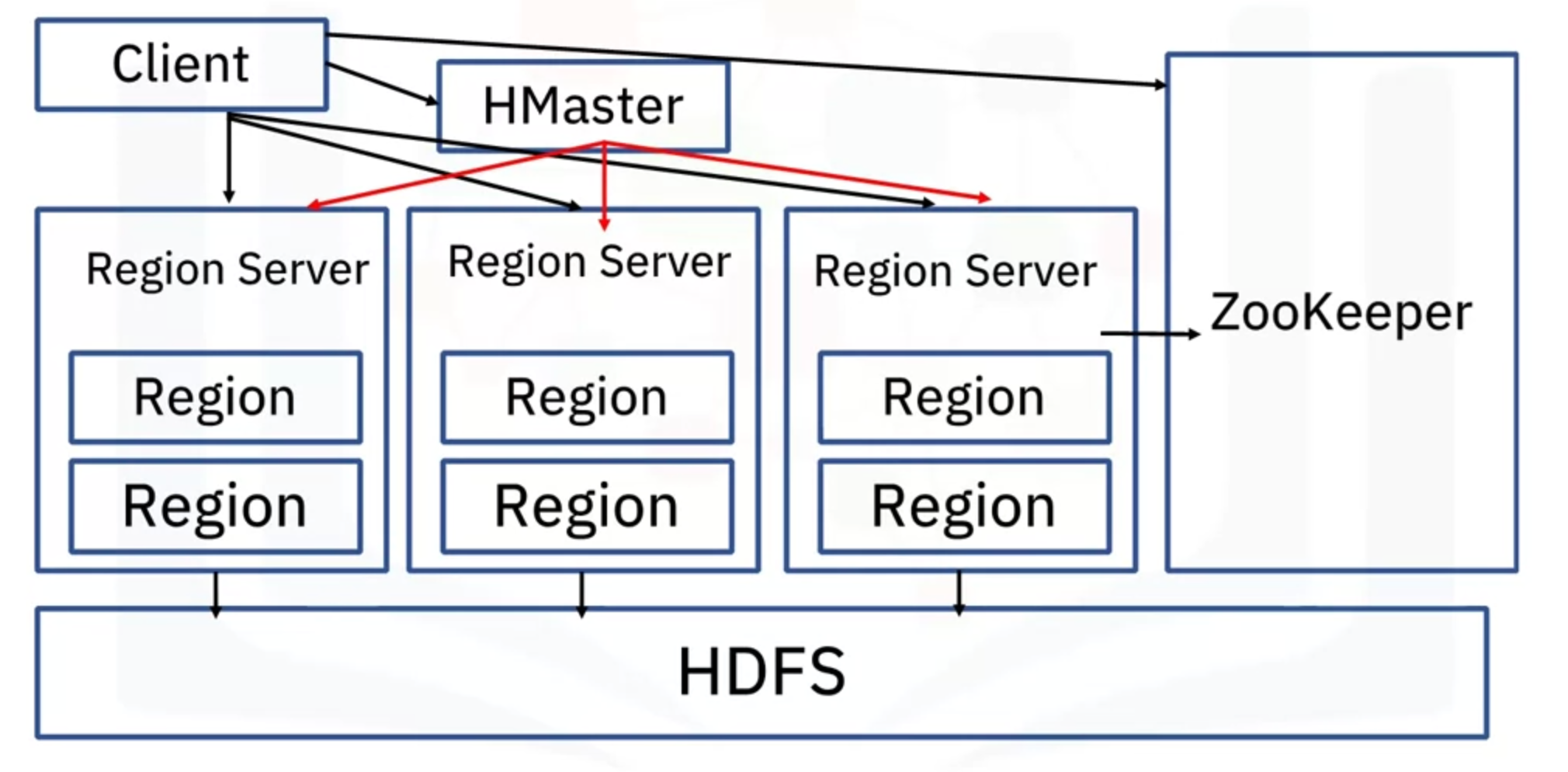
HBASE
- Columnar Non-Relational Database
- Write-heavy tasks
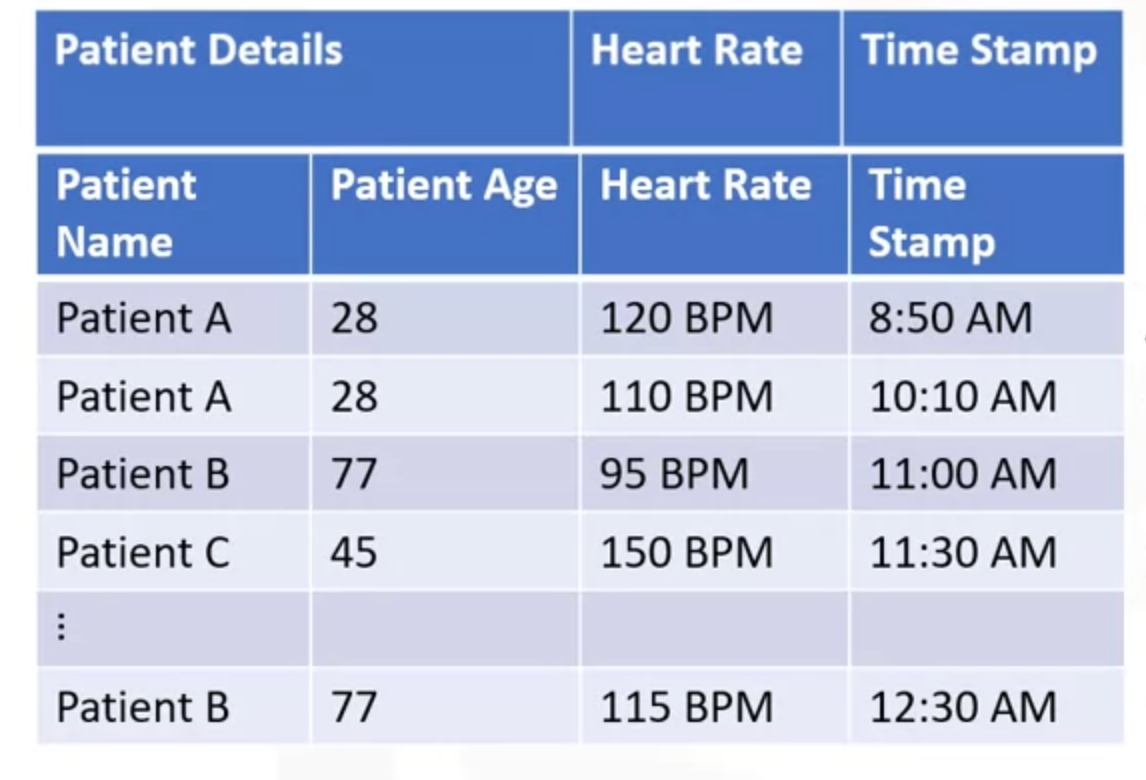
- We have to predefine column families. These columns are stored together
- The columns in the column family is flexible. We can add columns to a family at anytime
- In the above picture
patient_details, hear_rate, timestampare the column families.patiend_detailshas two columns namely -name, age